

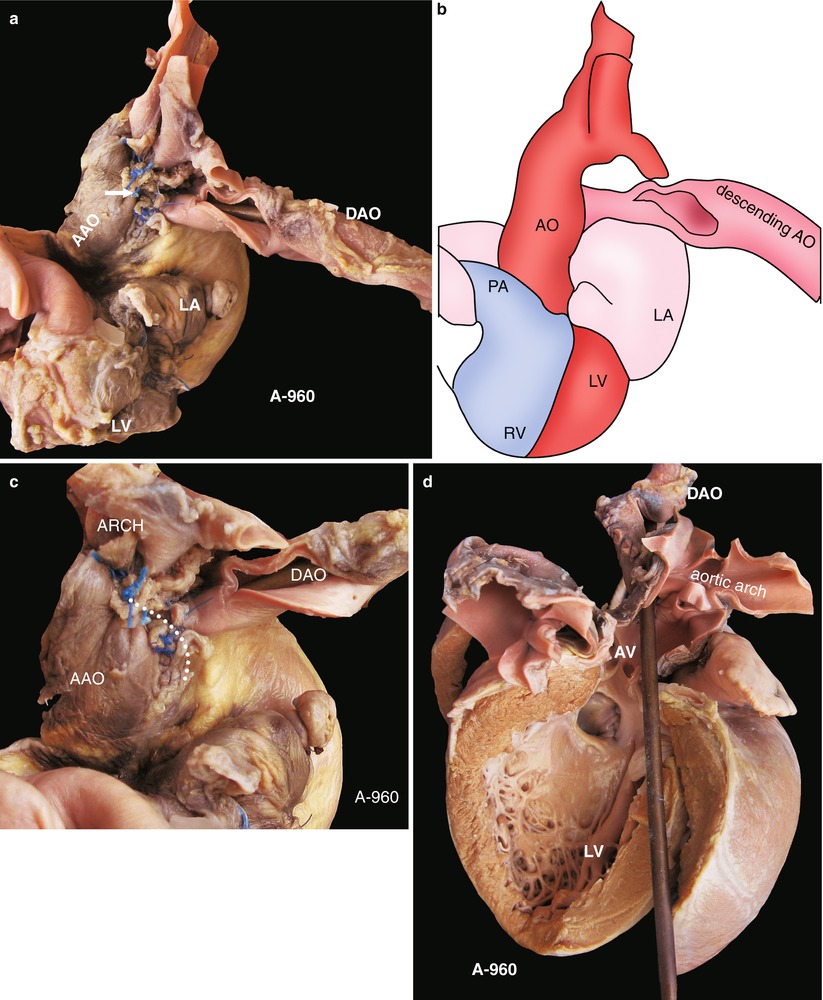
Prostaglandin E1 is necessary to start early to avoid sudden cardiac collapse and death. Serum calcium may be low in patients with DiGeorge syndrome. In addition to the imaging studies, all patients should have a fluorescence in situ hybridization since there is a high association with chromosome 22q11 deletion, which is associated with DiGeorge syndrome. These modalities are used to get a more comprehensive understanding of the lesion’s anatomy before surgical repair. Other imaging modalities used for the diagnosis of this entity are cardiac angiography, computed tomography angiography of the chest, and magnetic resonance angiography. The echocardiogram will define the site of the disruption. The electrocardiogram, typically, has nonspecific findings which include biventricular hypertrophy or right ventricular predominance. The chest radiograph will show cardiomegaly and increased pulmonary markings. The blood gas will reveal metabolic acidosis. When the diagnosis is suspected, it is imperative as initial work up to perform a blood gas, chest radiograph, electrocardiogram, and echocardiogram. Besides a ventricular septal defect, IAA can be associated with other more complicated cardiac anomalies for example, transposition of the great arteries, truncus arteriosus, aortopulmonary window, single ventricle, aortic valve atresia, right-sided ductus, and double-outlet right ventricle. Due to this malalignment, there could be left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. This lesion is present is approximately 73% of all cases. There is posterior malalignment of the conal septum additional to the interrupted aortic arch, producing a ventricular septal defect as an associated lesion. IAA is a ductus dependent lesion since this is the only way the blood flow can travel to places distal to the disruption. In an IAA, there is an anatomical and luminal disruption between the ascending and descending aorta. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can be considered the most severe form of aortic coarctation. Approximately 97% of babies born with a non-critical congenital heart disease have a life expectancy of one year of age, and approximately 95% are expected to live around 18 years of age.Ī rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients.
The survival rate of patients with congenital heart disease will depend on the severity, time of diagnosis, and treatment. the congenital heart disease represents approximately 4.5% of all neonatal deaths. In the United States, congenital heart disease affects 1% of births (40,000) per year, of which 25% have critical Congenital heart disease. It has an incidence of 8 cases of every 1000 live birth worldwide. Congenital heart disease is an abnormal formation of the heart or blood vessels next to the heart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
